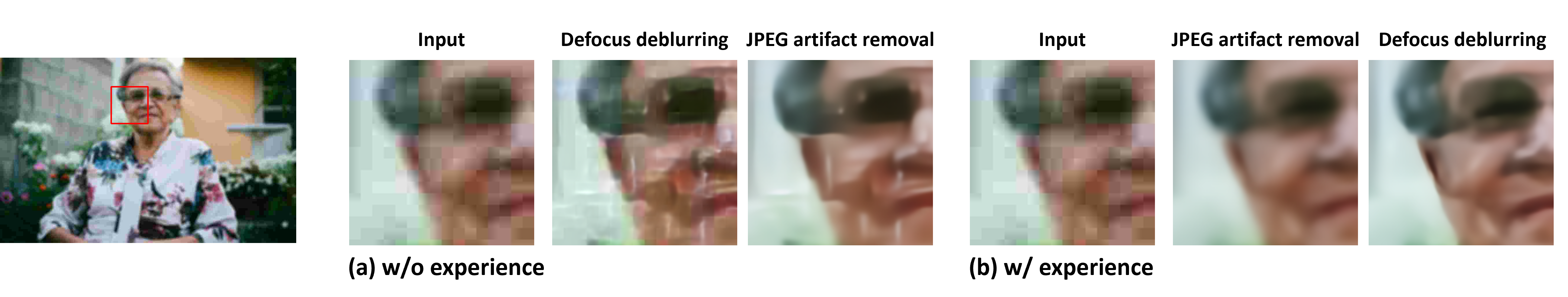Abstract
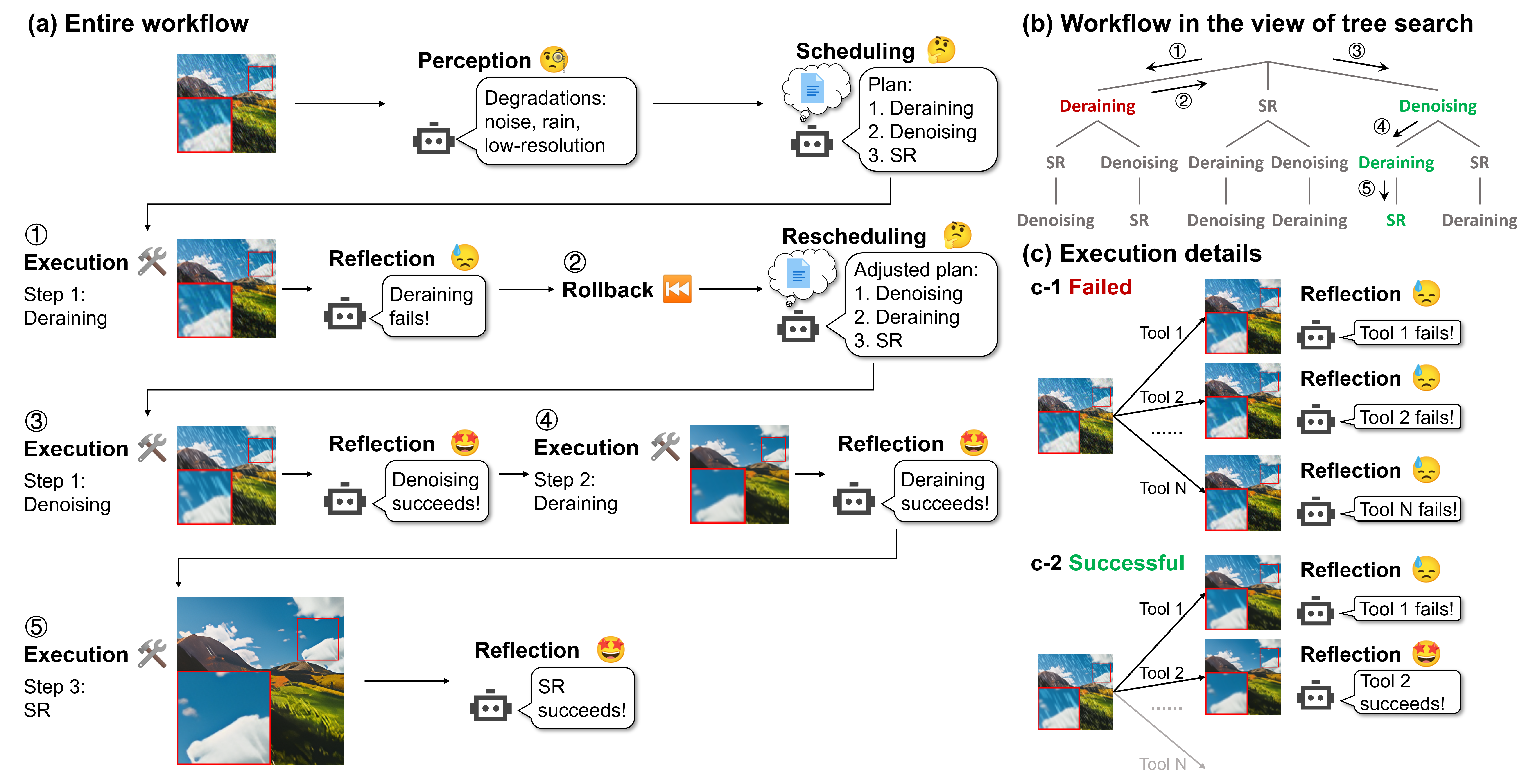
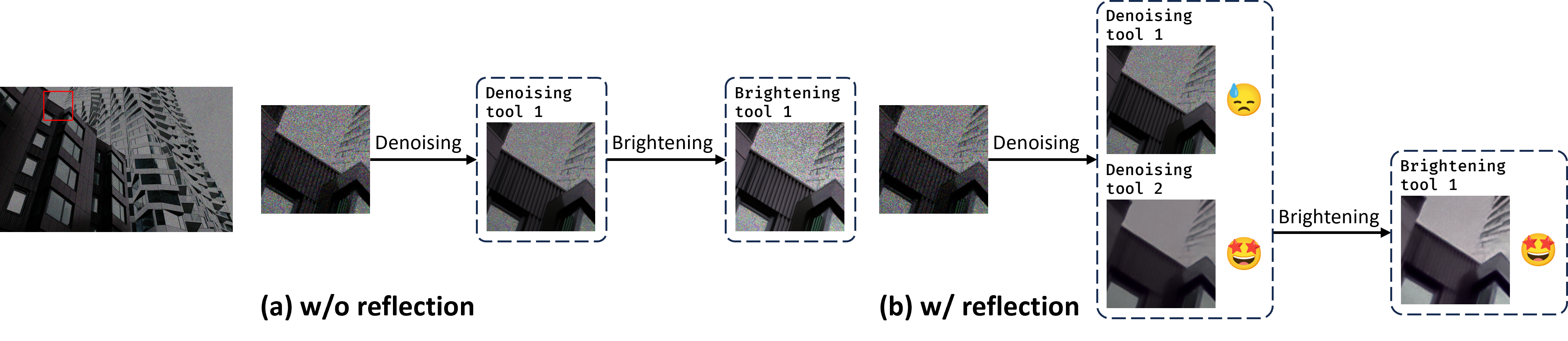
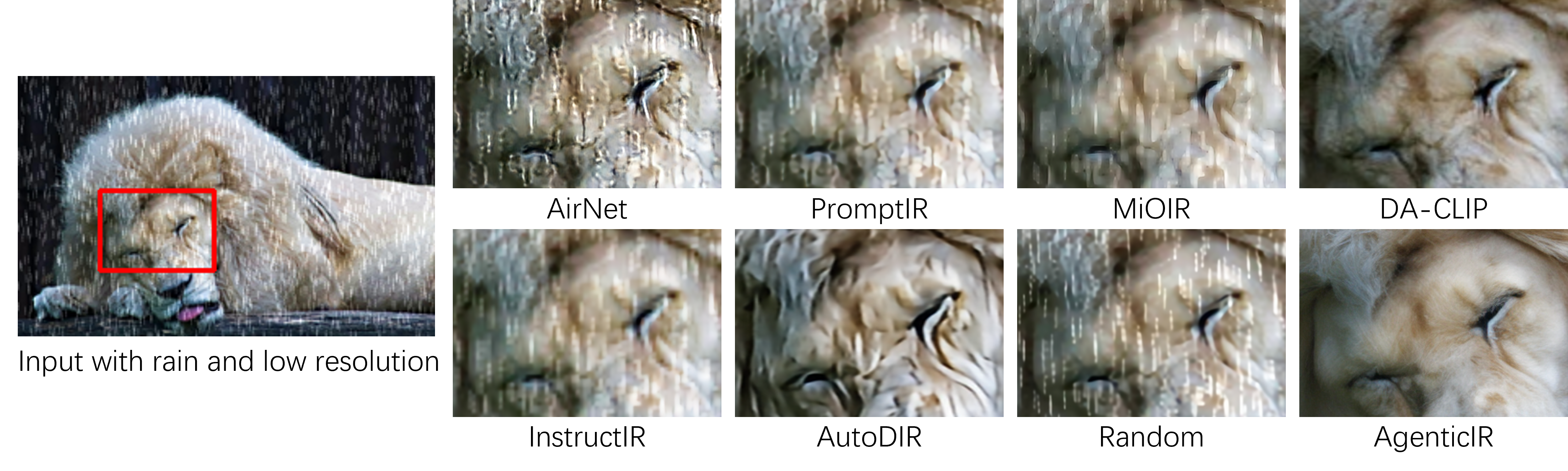
| Real-world image restoration (IR) is inherently complex and often requires combining multiple specialized models to address diverse degradations. Inspired by human problem-solving, we propose AgenticIR, an agentic system that mimics the human approach to image processing by following five key stages: Perception, Scheduling, Execution, Reflection, and Rescheduling. AgenticIR leverages large language models (LLMs) and vision-language models (VLMs) that interact via text generation to dynamically operate a toolbox of IR models. We fine-tune VLMs for image quality analysis and employ LLMs for reasoning, guiding the system step by step. To compensate for LLMs' lack of specific IR knowledge and experience, we introduce a self-exploration method, allowing the LLM to observe and summarize restoration results into referable documents. Experiments demonstrate AgenticIR's potential in handling complex IR tasks, representing a promising path toward achieving general intelligence in visual processing. | 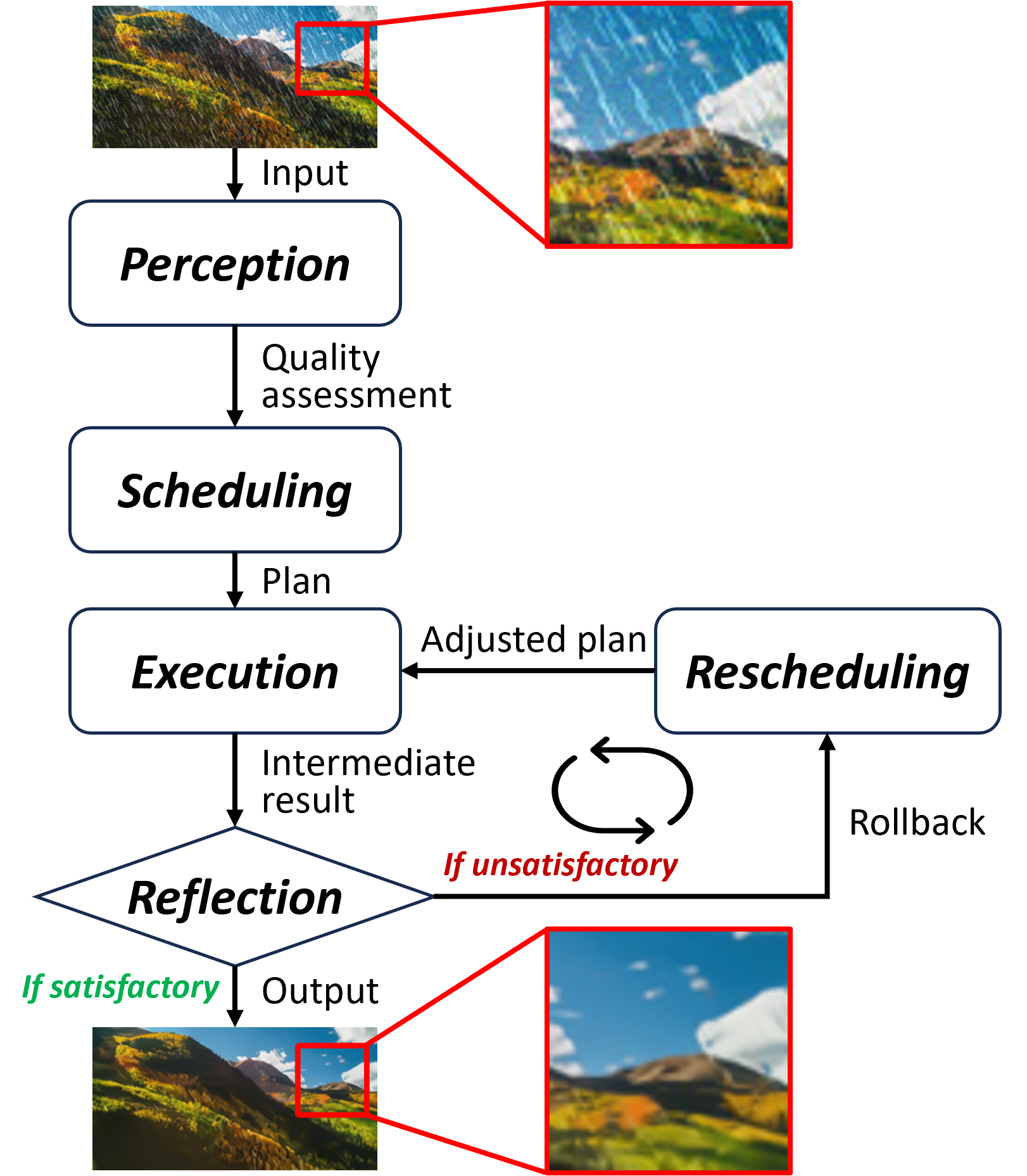 |